The Impact of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in Alcohol Addiction Treatment
Alcohol addiction is a complex condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide, leading to significant physical, emotional, and social consequences. The journey to recovery is often challenging, requiring a multifaceted approach to treatment. One effective method that has gained recognition is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT).
CBT is a form of psychotherapy that helps individuals understand and change unhealthy thought patterns and behaviors. In the context of alcohol addiction treatment, CBT plays a vital role in addressing the psychological triggers behind drinking habits and provides individuals with the tools necessary for long-term sobriety. We will explore how CBT impacts alcohol addiction treatment at private alcohol treatment center and the mechanisms that make it an essential part of the recovery process.
Understanding Cognitive Behavioral Therapy and Its Role
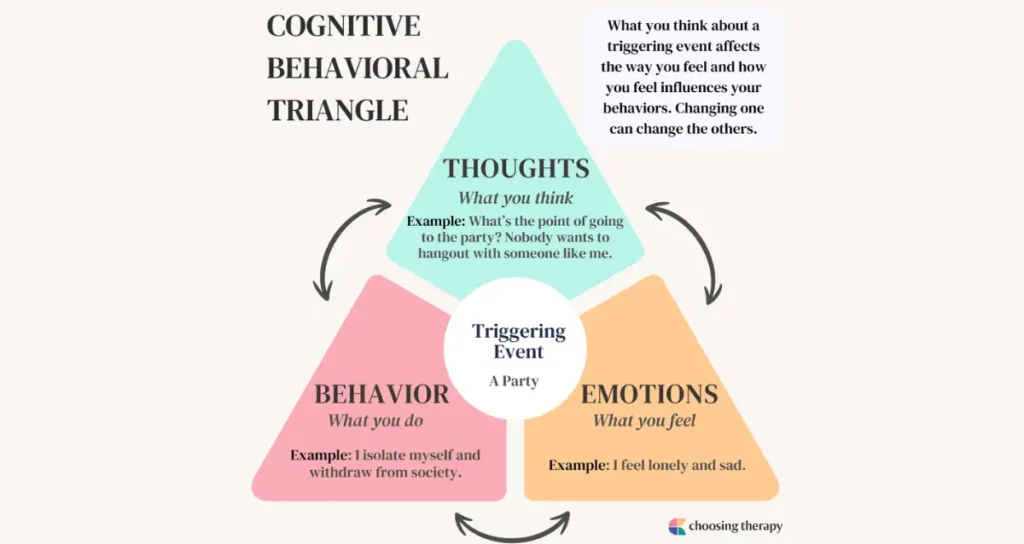
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy is based on the premise that our thoughts, emotions, and behaviors are interconnected. Individuals can change their behavior and improve emotional well-being by identifying and challenging negative thought patterns. In the context of alcohol addiction, CBT helps patients recognize the thoughts and feelings that lead to drinking.
For example, individuals may drink to cope with stress, anxiety, or feelings of inadequacy. CBT enables patients to confront these thoughts and develop healthier coping mechanisms. It also helps them understand the consequences of alcohol use, both short-term and long-term, providing them with a clearer perspective on the benefits of sobriety. This understanding allows individuals to develop a sense of control over their actions, empowering them to make healthier decisions.
The Impact of CBT on Relapse Prevention
One of the major challenges in alcohol addiction recovery is the risk of relapse. Many individuals struggle to maintain sobriety due to the presence of triggers that cause them to revert to old drinking patterns. CBT helps individuals identify these triggers, whether social situations, stressors, or emotions, and develop strategies to manage them.
By teaching skills such as problem-solving, emotional regulation, and stress management, CBT helps individuals avoid situations where they might be tempted to drink. Furthermore, CBT encourages individuals to restructure their thoughts, challenging the notion that drinking is the only or best way to cope with life’s challenges. Over time, individuals can build resilience, making them less vulnerable to relapse.
CBT’s Focus on Self-Efficacy and Personal Accountability
A critical component of CBT in alcohol addiction treatment is its focus on enhancing self-efficacy, or the belief in one’s ability to handle challenges and achieve goals. This focus is essential in addiction treatment because alcoholics often feel powerless or incapable of changing their habits.
CBT helps individuals gain confidence in their ability to navigate difficult situations without turning to alcohol. It encourages personal accountability, where individuals are taught to take responsibility for their thoughts, emotions, and actions. This sense of responsibility is crucial for long-term recovery, as it fosters a mindset of self-control and resilience. Individuals learn to make positive choices, even in the face of adversity.
Behavioral Modifications Through CBT Techniques
CBT provides individuals with practical tools to address their alcohol addiction. Individuals can make meaningful changes in their behaviors through various techniques such as cognitive restructuring, behavioral activation, and exposure therapy. Cognitive restructuring involves identifying and challenging irrational or distorted thoughts and replacing them with more balanced and realistic thoughts.
For example, a person might believe that they cannot relax without alcohol, but CBT helps them reframe this belief by introducing alternative relaxation techniques. Behavioral activation encourages individuals to engage in enjoyable and fulfilling activities, reducing the temptation to drink out of boredom or emotional distress. Exposure therapy helps individuals gradually confront situations where alcohol is present, teaching them to manage their responses without drinking. These techniques allow individuals to break free from habitual drinking patterns and establish new, healthier behaviors.
Enhancing Motivation for Change Through CBT
Motivation is a key factor in the success of alcohol addiction treatment. Without a strong desire to change, it is difficult for individuals to overcome their addiction. CBT plays a crucial role in enhancing motivation for recovery. Through motivational interviewing, a technique commonly used in CBT, individuals explore their ambivalence about drinking and identify the reasons they want to quit. This process helps individuals strengthen their commitment to sobriety.
CBT also reinforces the concept of rewards and consequences. By focusing on the positive outcomes of sobriety, such as improved health, relationships, and financial stability, individuals are more likely to remain motivated throughout their recovery journey. The sense of achievement and personal growth that comes with overcoming addiction fosters a sense of purpose, which in turn strengthens their resolve to maintain a sober lifestyle.
Integrating CBT with Other Treatment Approaches
While CBT is a powerful tool in alcohol addiction treatment, it is often most effective when integrated with other treatment approaches. In many cases, individuals receive a combination of psychotherapy, medication, and support groups. At Hollywood hills rehab center, individuals receive a comprehensive program combining psychotherapy, medication, and support groups, fostering a holistic path to recovery.
Medication-assisted treatment (MAT) can help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms, while support groups such as Alcoholics Anonymous provide a sense of community and shared experience. When combined with CBT, these approaches work synergistically to address the physical, psychological, and social aspects of addiction.
For example, while CBT helps individuals manage their thoughts and behaviors, MAT can address the biological components of addiction, making it easier for individuals to stay sober. Integrating these approaches provides a holistic and comprehensive treatment plan that increases the likelihood of long-term success.
Conclusion
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy plays a significant role in alcohol addiction treatment by addressing the psychological and behavioral components of addiction. Through techniques that challenge negative thought patterns, teach coping strategies, and enhance self-efficacy, CBT empowers individuals to regain control over their lives.
By focusing on relapse prevention, motivation, and long-term behavior change, CBT helps individuals achieve and maintain sobriety. When integrated with other treatment approaches, such as medication and support groups, CBT offers a comprehensive and holistic approach to recovery. Ultimately, the impact of CBT in alcohol addiction treatment extends beyond the treatment period, providing individuals with the tools they need to live a fulfilling, sober life.







